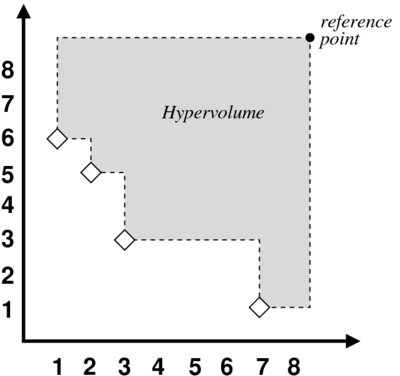
Computation of the Hypervolume Indicator
WARNING:This code is not maintained and only kept for reproducibility purposes. You can find a more recent and modern implementation of this code here: https://github.com/multi-objective/moocore
Introduction
The performance assessment of algorithms for multiobjective optimization problems is far from being a trivial issue. Recent results indicate that unary performance measures, i.e. performance measures which assign a single value to each non-dominated point set, are inherently limited in their inferential power. Despite these limitations, the hypervolume indicator (also known as Lebesgue measure or S metric) is still considered to possess some reasonable properties, having also been proposed as a guidance criterion for accepting solutions in Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithms. Therefore, the computational time taken for computing the hypervolume indicator is a crucial factor for the performance of such algorithms.
This program implements a recursive, dimension-sweep algorithm for computing the hypervolume indicator of the quality of a set of n non-dominated points in d dimensions. It also incorporates a recent result for the three-dimensional special case. The proposed algorithm achieves O(nd-2 log n) time and linear space complexity in the worst-case, but experimental results show that the pruning techniques used may reduce the time complexity even further. The program assumes that all objectives must be minimized. Maximization objectives may be multiplied by -1 to convert them to minimization.
Relevant literature:
- [1]
- Carlos M. Fonseca, Luís Paquete, and Manuel
López-Ibáñez. An improved dimension - sweep
algorithm for the hypervolume indicator. In Proceedings of the
2006 Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC'06), pages
1157–1163. IEEE Press, Piscataway, NJ, July 2006.
[ bibtex | doi: 10.1109/CEC.2006.1688440 | PDF | software ] - [2]
- Nicola Beume, Carlos M. Fonseca, Manuel
López-Ibáñez, Luís Paquete, and
J. Vahrenhold. On the complexity of
computing the hypervolume indicator. IEEE Transactions on
Evolutionary Computation, 13(5):1075–1082, 2009.
Building
In GNU/Linux, the program can be compiled from source by invoking
make
The command-line tool can now be compiled in Windows with the GCC version provided by MINGW.
We recommend that you compile it specifically for your architecture.
Depending on the compiler and version of the compiler you use there are
different ways to achieve this. For recent GCC versions, make
will pick a suitable -march argument based on the processor of
the build machine. This can be overridden by passing an MARCH=
argument to make. Similarly if you use the Intel C compiler, it
will pick a sensible default architecture (-xHOST) for you. If
you want to override this, pass XARCH= to make. So
to build for an Intel Core2 you would use
make MARCH=core2
if you are using the GCC compiler and
make XARCH=SSSE3
for the Intel C compiler. Generally make will try to pick
good flags for you, but if you need to, you can override them by passing a
OPT_CFLAGS argument to make. To build an unoptimized version of
hv you could run:
make OPT_CFLAGS="-O0 -g"
Finally, if you do not want to see the command line of each compiler
invocation, pass S=1 to make.
Usage
The program reads a set of points provided by filenames in the command line:
hv data
or standard input:
cat data | hv
In the input files, each point is given in a separate line, and each
coordinate within a line is separated by whitespace. An empty line denotes a
separate set. (See also the --union option). The program
assumes that all objectives must be minimized. Maximization objectives may
be multiplied by -1 to convert them to minimization.
A reference point can be given by the option -r.
hv -r "10 10 10" data
If no reference point is given, the default is the maximum value for each coordinate from the union of all input points.
For the remainder options available, check the output of hv
--help.
License
This software is Copyright (C) 2006-2014 Carlos M. Fonseca, Manuel López-Ibáñez, Luís Paquete and Andreia P. Guerreiro.
This program is free software (software libre); you can redistribute it
and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License,
or (at your option) any later version. As a particular exception, the files
hv.c and hv.h may also be redistributed and/or
modified under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) as
published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 3 of the License,
or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Please be aware that the fact that this program is released as Free Software does not excuse you from scientific propriety, which obligates you to give appropriate credit! If you write a scientific paper describing research that made substantive use of this program, it is your obligation as a scientist to (a) mention the fashion in which this software was used in the Methods section; (b) mention the algorithm in the References section. The appropriate citation is:
Carlos M. Fonseca,
Luís Paquete, and Manuel López-Ibáñez.
An improved
dimension - sweep algorithm for the hypervolume indicator. In
Proceedings of the 2006 Congress on Evolutionary Computation
(CEC'06), pages 1157–1163. IEEE Press, Piscataway, NJ, July
2006.
Moreover, as a personal note, I would appreciate it if you would email
manuel.lopez-ibanez with citations of papers referencing this
work so I can mention them to my funding agent and tenure committee. manchester.ac.uk
manchester.ac.uk
Download
- This is a BETA release for testing. Please be sure to compare your results with the stable 1.3 version and report to us any differences.
- The files
hv.candhv.hare now also licensed under the GNU LGPL, which allows calling to the function that computes the hypervolume (See section "Embedding" in the README file) from other software that uses a license incompatible with the GNU GPL.
- This is a BETA release for testing. Please be sure to compare your results with the stable 1.3 version and report to us any differences.
- Andreia P. Guerreiro has improved the integration of the 3D case with the rest of the algorithm, which leads to significant reduction of computation time. She has also enhanced the numerical stability of the algorithm by avoiding floating-point comparisons of partial hypervolumes.
- The command-line tool can now be compiled in Windows with the GCC
version provided by MINGW. (The function that
computes the hypervolume is ANSI C and it is self-contained in the file
hv.c, See section "Embedding" in the README file for how to use it in your applications).
- The hypervolume is now calculated separately for each input set.
Reading from standard input when using the option
--unionemulates the previous behaviour. - Fix bug caused by uninitialized memory. Thanks to Andreia P. Guerreiro for reporting this.
- Warn about discarding points that do not strictly dominate the reference point. Previous versions did not discard such points and may compute a wrong value.
- New options:
-u, --union treat all input sets within a FILE as a single set. -s, --suffix=STRING Create an output file for each input file by appending this suffix. This is ignored when reading from stdin. If missing, output is sent to stdout. - Guillaume Jacquenot contributed a MEX interface for MATLAB
(
Hypervolume_MEX.c). Use `make mex` to compile it. - Olaf Mersmann contributed a new build system that should work in Windows, Linux, Darwin (OS X), and using GCC, ICC, Sun C compiler and other compilers, as long as GNU Make is available. See section "Building" in the README file.
- The function that computes the hypervolume is now called
fpli_hv()and it is compiled into a separate libraryfpli_hv.athat can be linked with other C/C++ applications. See section "Embedding" in the README file. Thanks to Olaf Mersmann for this suggestion.
- Fix off-by-one error in loop iteration caused by repeated
coordinates and producing inconsistent results. (Thanks to Yuji Sakane for reporting this).
- Compute hypervolume for two-dimensional data using 2D algorithm
even if recursion is set to stop in dimension 3.
- Basic compilation:
make march=pentium - Select one of the variants (1, 2, 3, or 4) described in the paper
[1]:
make march=pentium VARIANT=4 - Usage:
hv [OPTIONS] [FILE...]Calculate the hypervolume of the union set of all input FILEs. With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input. Options: -h, --help print this summary and exit. --version print version number and exit. -v, --verbose print some information (time, input points, output points, etc). Default is --quiet. -q, --quiet print just the hypervolume (as opposed to --verbose). -r, --reference=POINT use POINT as reference point. POINT must be within quotes, e.g., "10 10 10". If no reference point is given, it is taken as the maximum value for each coordinate from the input points. -1, --stop-on-1D stop recursion in dimension 1 -2, --stop-on-2D stop recursion in dimension 2 -3, --stop-on-3D stop recursion in dimension 3 (default)
Projects using this software
- mco: R package of multi criteria optimization algorithms and related functions.
- emoa: R package of evolutionary multiobjective optimization algorithms.
- Edgar Reehuis. Multiobjective Robust Optimization of Water Distribution Networks. Master's thesis, Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science, Leiden University, The Netherlands, 2010.
- MOO-EALib (Shark): An extension of the EALib for multi-objective optimization. Part of the C++ Shark library for the design and optimization of adaptive systems.